Network Security Best Practices
Network security is no longer regarded as an afterthought; it has become an essential element that aids in an organization’s sustainability. While foundational network security best practices establish a solid baseline of security, securing against common threats and vulnerabilities, advanced practices ensure proactive protection and quick incident response.
Foundational network security best practices
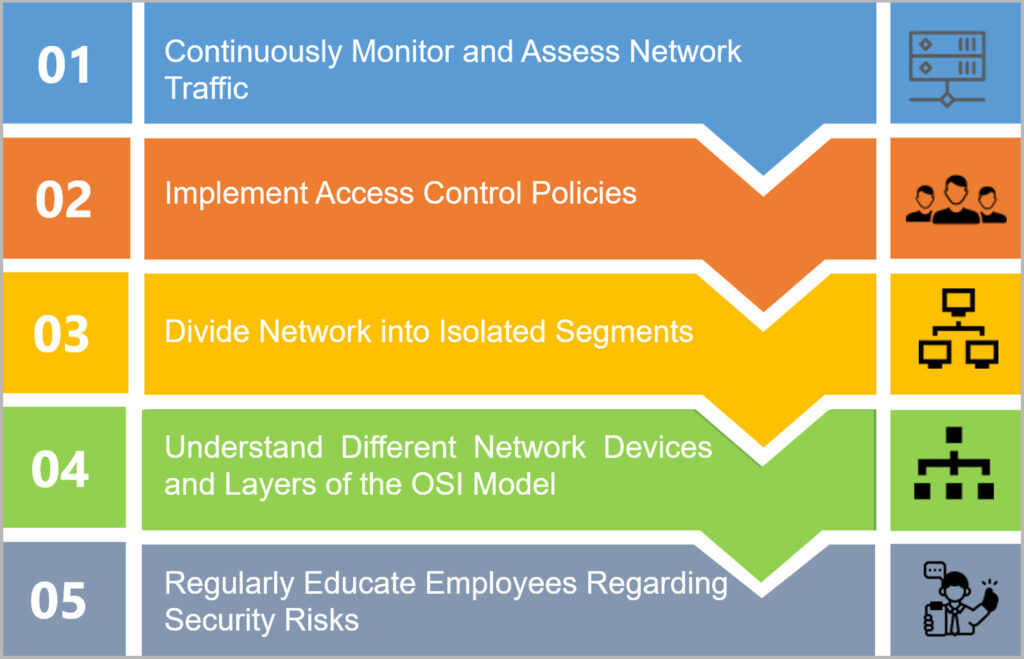
Network visibility
Network visibility lets organizations have a better knowledge of the behavior of traffic on their networks. Organizations can implement the awareness to improve the efficiency, security, and performance of those networks.
Utilize policy-based access control
Policy-based access control decreases vulnerabilities and ensures authorized users access resources in a controlled manner.
Implement network segmentation
Network segmentation minimizes security risks by forming a multi-layer attack surface that prevents lateral network attacks. Consequently, even if attackers breach the organization’s first perimeter of defense, they are contained within the network segment they access.
Maintain familiarity with network device types and understand the OSI model
Knowing network device types assists in configuring security measures precisely. It helps in addressing vulnerabilities specific to each device category effectively. OSI model comprises seven functional layers that provide the foundation for communication among computers over networks. Understanding the OSI model assists in pinpointing vulnerabilities, enabling precise security measures across layers, and strengthening network defense comprehensively.
Provide employee training and awareness
Employee training contributes to efficient threat detection and emphasizes the significance of proactive security measures.
Additional network security best practices that should not be overlooked
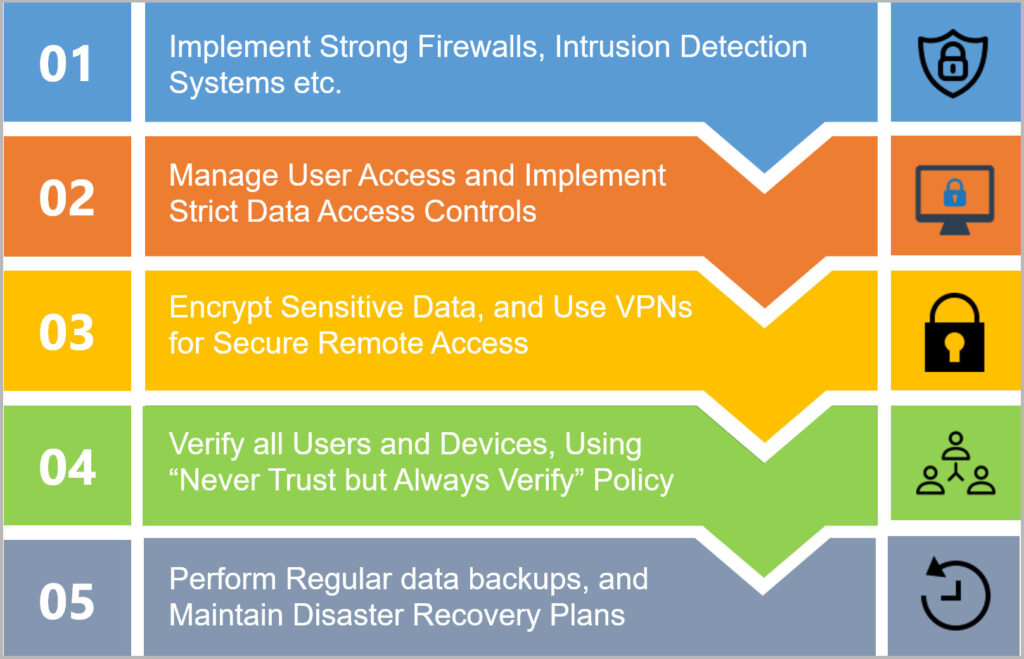
Know Network Defenses
Imagine this scenario. The IT team of an e-commerce enterprise lacks a thorough understanding of network defenses beyond firewall utilization. There are chances of failing to identify a breach until customers start reporting suspicious activities. Knowing network defenses including intrusion detection systems is important for organizations to form a powerful security framework.
Secure network from insider threats
Traditional cybersecurity strategies generally prioritize defending the network from external forces. However, this can lead to internal blind spots, which may pose the risk of insider threat. Protecting networks from insider threats is essential for organizations to secure against intentional and accidental data breaches.
Use encryption and VPNs
A healthcare organization cannot afford to compromise on confidentiality of patient information just because remote employees access patient records from public Wi-Fi without a VPN, leading to a hacker intercepting their communications. The employees’ data would be encrypted and tunneled securely, preventing unauthorized access and maintaining confidentiality with the availability of a VPN.
Deploy zero trust
Zero trust is not just about user identity, segmentation, and safe access. It encompasses continuous monitoring, strict access controls, and validating every action irrespective of user location. This concept assumes no implicit trust; its underlying principle is “Never trust, but always verify”.
Perform regular data backups and maintain disaster recovery plans
Frequent data backups and disaster recovery plans are essential for network security as they ensure quick recovery from cyber incidents. During a breach or data loss, backups assure data integrity and operational continuity. Disaster recovery plans provide systematic steps in quickly responding to cyber incidents and minimize downtime, data loss, and operational disruptions.
Incorporate powerful network security with FatPipe MPVPN’s MPSec (multi-path security) which provides better security of data transmission over data connections. Improve safety through seamless encryption (Transport Layer Security technology), ensuring data integrity.