What is it, and where is it going?
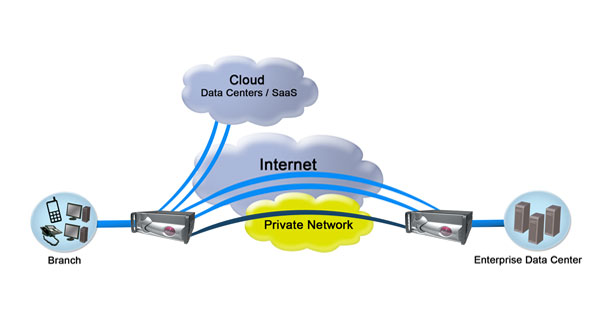
Most WANs of today still use routers and technology that, at
the time, served a purpose and provided a mechanism to expand the network to
remote branches and locations across the world using MPLS or similar protocols.
But times have changed.
Traffic on WANs has increased by almost 10 fold in the last 15
years. T1 was “revolutionary” many years
ago, providing speeds of a blistering 1.5Mb/s. Today, this throughput is not going to make
the grade in 99% of WANs. Fiber, or
optical networks can reach speeds of over 100Gbps. It is like buying a new car every 5
years. You see the features and you
want them, as do network administrators.
So what is the “Intelligent Edge?”
First, what really is “the edge”? A definition from Wikipedia is “an edge
device provides an entry point into enterprise or service provider core
networks. It can be thought of as a
router that provides authenticated access to faster more efficient backbone and
core networks.” Essentially, “the
edge” of any network is thought of to be a place where you generate, collect,
and analyze data on the edge of the network where the data is generated rather
than in centralized servers and systems.
Computation is largely or completely performed on a distributed device
node known as smart device or edge device.
OK – so now we understand “what” the edge is, so what is the
“intelligent edge? As Wide Area
Networks grew and became more complicated with more and more devices being
attached, both hard wired, wireless and remote, the need for bandwidth
increased, dramatically.
Today – there are almost 24 Billion devices connected to the
internet with the expectation of 50 billion by 2020. Think of the “intelligent Edge” as a place
where computing occurs. It is
“intelligent” because there is technology there that has ability to control,
analyze and compute. This can be a
manufacturing floor, a farm crop field, a city, your home, power plant, sports
arena, your car, in the air, or under the sea.
These interrelated computing devices or objects are referred to as the
Internet of Things (IoT) and these devices are driving how and why the “intelligent
edge” is becoming a key focus for network managers. This
intelligent edge connects these devices, performs analytics, computes, and can
control actions that were formerly confined to the central or cloud based data
centers.
The usage and access demand is what is driving “edge”
technologies and solutions. It is much
better to access the information and data as close to the connection point as
possible.
On average, users have 5 different devices to attach to the
network. Of course they expect to
attach to a network and access the applications and data they need,
instantly. But this requires a network
with agility, flexibility and “intelligence” to understand where the requests
are coming from, how to manage the requests in the most efficient and effective
manner possible and to provide reliable connectivity which, after all, is why
sensors and monitors are being installed in machines such as wind turbines, to monitor
vibration, wear and operating effectiveness, and help prevent brownouts or
blackouts. However, without constant
and reliable connectivity, the data provided by these sensors would be “lost”.
The un-intelligent router in all its forms is struggling to
find relevance in this scenario. The availability of ethernet handoff is
killing the router business. They are trying hard to find relevance in this
scenario.
So where next for the “intelligent edge”?
As stated earlier, more and more devices are being connected
and more and more data being collected on a multitude of things to help
streamline decision making to prevent downtime or in the worst cases,
failure.
Networks of the future are going to be driven by the need
for instant information, instant decisions, and instant remediation. All of which is why the “intelligent edge”
will become a mainstream “product” in the design and implementation of ANY
network. Having said that, what does
this mean for networks of today, and what should the administrators plan for to
embrace these changes?
Let’s look at the current most important issues faced by
network administrators and how embracing intelligent edge devices will affect
how these issues might be dealt with.
Firstly – Security:
Many recent surveys suggest the number one issue faced by
network administrators worldwide is, security.
Security of data, whether in transmission or stored somewhere is
critical. We just have to look at the problems faced
with social media company data breaches, credit card company breaches and
others to know that data security is by far and away the number one issue. Can the “intelligent edge” help? Yes and no.
It is not the “edge’ that can prevent hacking, it is the underlying
software that transmits the data that is key.
The transmission of data across the network, from edge device or user to
data center to other devices, needs to be secure. Administrators need to deploy software
solutions that provide highly secure data transmission, and that includes data
from the edge. The intelligent edge,
does however, compute locally and provides a more local management issue, rather
than a broad network security issue.
Second:- Ease of
Management:
Believe it or not, the costs of recruiting, training,
certifying and managing skilled IT staff is becoming a major issue for any
business. The days of paying for
continuing education and propriety certification are waning. Today, administrators are looking for
solutions that are easy to manage, especially when devices and or offices are
remote. The Intelligent Edge should be
simple, easy to install and manage remotely, and for the most part, this is
true once the devices are installed.
Third: –
Compatibility with existing networks:
Organizations are reluctant to rip and replace their
networks. If a solution can augment
existing installations, administrators will look favorably at these
recommendations. So, does the
intelligent edge help with these decisions?
Certainly, as they can use existing infrastructure provided there is an
underlying software that can manage data transmission and device access
securely and reliably.
Fourth: – Network
performance:
Latency, bandwidth, reliability, duplication and overall
cost of the network are all top of mind.
Intelligent edge devices cannot perform or provide the benefits they
claim to bring to a business if the underlying network is slow, unreliable or
using legacy systems that are slow and difficult to manage or update. The Intelligent Edge is only going to be as
good as the network infrastructure it is connected to. The bottom line here is to make sure the
network is configured to take advantage of intelligent edge device data.
So now what?
The Intelligent Edge is certainly something that can help network
administrators predict the future more accurately. The more data these devices provide, the
better the decision will be on how to use this information, and with the advent
of AI, this information can be acted on immediately, providing “instant”
remediation or feedback that helps businesses learn what we like, when
equipment may malfunction, where to route data to avoid a line failure, how to
prepare for the best solution, and even where we might choose to travel to
next.
So just install intelligent edge devices and move
on? Stop! Read this first!
Earlier in this article, we mentioned the need for the
underlying network infrastructure to be “intelligent edge” ready. Remember, you can have all the sensors and
monitoring services available, but if the data they produce is not getting to
the right places at the right time, you are back to square one. Adding more devices or “edge services” does
not make network administration easier unless you have the right network
solution to take advantage of these benefits.
Without installing software solutions to monitor and manage
your edge devices, the “intelligent edge” becomes another user on the
network. In order to take advantage of
the many benefits the “intelligent edge” provides, you need to make sure your
network is ready.
It must be ready to:
- Transmit data from all devices, including the
intelligent edge devices, securely and effectively, without user intervention.
- Proactively route data on the best available
link in times of congestion
- Automatically failover in a sub second if a
connection should fail
- Use all and available bandwidth proactively and
intelligently, without having to reconfigure the network
- Automatically detect and remediate attempts to
breach the security of the network
- Be managed easily and simply from a single
point, with zero touch provisioning for remote branches.
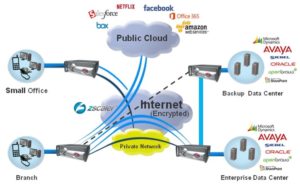
FatPipe Networks has been providing network solutions for
over 15 years and is the only company with a patented security module that is
FIPS 140-2 certified, providing military grade security for traffic across the
WAN or across broadband networks.
FatPipe solutions give administrators the comfort of the highest SD-WAN
security available.
Fatpipe patented technologies have eliminated the need for
BGP routing, and with it all the delays in inefficiencies of route propagation.
Fatpipe brought intelligence to the edge.
Using FatPipe’s single pane GUI management tools,
administrators can not only see exactly what their network looks like, but with
FatPipe’s QoS, they can prioritize application access no matter where the
application resides, in the cloud or locally.
In addition, FatPipe’s solutions allow for load balancing over multiple
links, including Cable, DSL, MPLS, DIA, 3G, 4G, 5G LTE and satellite. FatPipe’s management tools are easy to use,
requiring basic IT skills saving companies’ significant time and IT staff
educational costs.
FatPipe has always been a company serving network administrators. FatPipe was providing WAN SD-WAN solutions long before SD-WAN became a buzz word. The solutions are built to work with existing LAN and WAN infrastructures and protocols. In fact, FatPipe is the only SD-WAN vendor to support up to 40Gbps bandwidth and up to 15 interfaces.
FatPipe Networks:
801-683-5656 x1224.